A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Insulation Materials for Walls
Heat insulation for walls plays a vital role in improving energy efficiency, reducing heating and cooling costs, and maintaining indoor comfort. Let’s explore the most common types of heat insulation materials in detail.1. Mineral Wool (Rock Wool and Glass Wool)
Mineral wool is manufactured from molten natural rock or recycled glass, making it an eco-friendly choice.
- Applications: Used in cavity walls, external cladding systems, and internal partitions.
- Properties:
- High thermal resistance due to its fibrous structure.
- Excellent soundproofing and fire resistance.
- Can withstand temperatures up to 1,000°C (rock wool).
- Installation: Typically fitted between wall frames or behind cladding, often combined with vapor barriers to prevent moisture penetration.
- Drawbacks: Mineral wool can absorb moisture if not properly sealed, reducing its effectiveness.
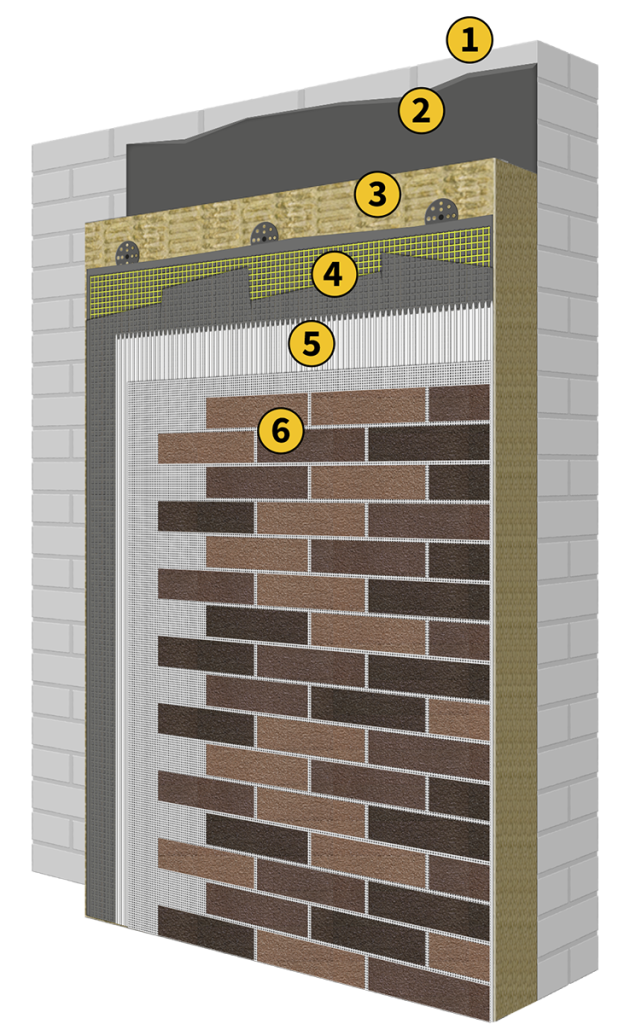
It adds an extra layer of protection, ensuring resistance to outer impacts like weather, mechanical stress, and temperature changes. This combination enhances the overall insulation system, improving energy efficiency and maintaining structural integrity.
Additionally, AMK’s lightweight and flexible design simplify installation, making it a practical solution for facades that require high thermal and acoustic performance without compromising aesthetics.
Scheme of installation of AMK on mineral wool
- Wall
- Adhesive mortar
- Mineral wool insulation batt
- Basecoat and Reinforcement Mesh
- White tile glue
- AMK
2. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material that provides excellent thermal insulation.
- Applications:
- EPS: Commonly used in External Wall Insulation (EWI) systems.
- XPS: Suitable for high-pressure applications like basement walls or floors.
- Properties:
- EPS offers better affordability but lower density compared to XPS.
- XPS is more durable, waterproof, and resistant to compression.
- Drawbacks: Both types require fire-resistant treatments, as untreated polystyrene is flammable.
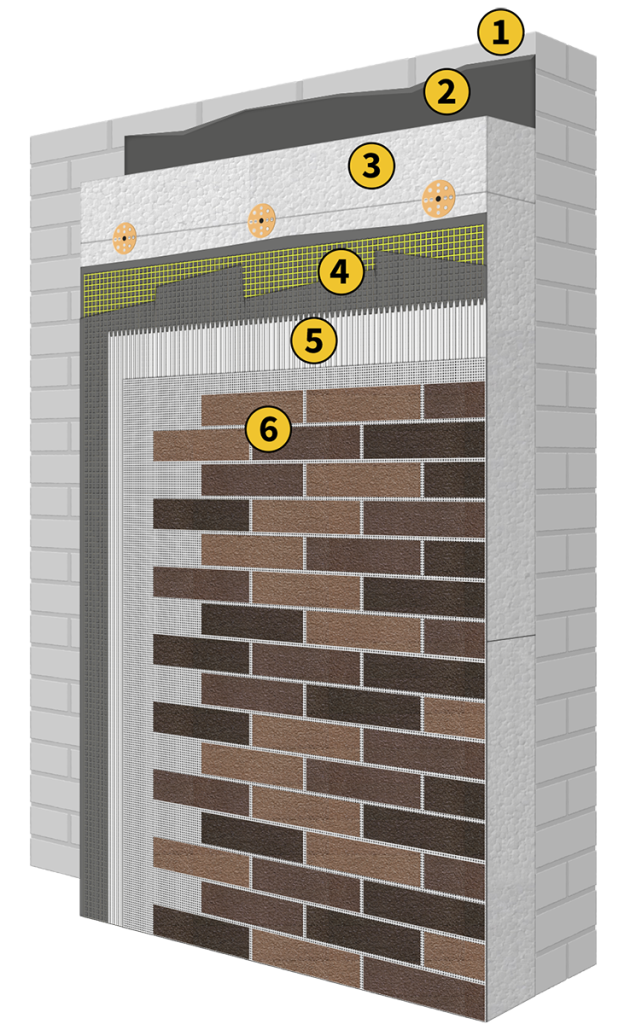
AMK Decorative Covering is an ideal solution for installation on EPS (expanded polystyrene) and XPS (extruded polystyrene) insulation boards.
It enhances the protective layer, offering excellent resistance to external impacts, weather conditions, and mechanical stress. The lightweight nature of AMK prevents excessive strain on insulation boards, maintaining their structural integrity.
Its flexibility allows for easy installation, ensuring seamless coverage. By applying AMK over EPS and XPS, you create a highly efficient, insulated, and visually appealing facade that combines functionality with modern aesthetics.
Scheme of installation of AMK on EPS/XPS board
- Wall
- Adhesive mortar
- EPS/XPS insulation board
- Basecoat and Reinforcement Mesh
- White tile glue
- AMK
3. Polyurethane Foam (PU Foam)
This spray-applied insulation is ideal for irregular surfaces and hard-to-reach spaces.
- Applications: Suitable for internal cavity walls and areas requiring airtight insulation.
- Properties:
- Extremely low thermal conductivity (0.020-0.030 W/m·K).
- Provides an airtight seal that prevents air infiltration.
- Drawbacks: PU foam is relatively expensive and less eco-friendly due to the chemicals used in its production.

AMK Decorative Covering is well-suited for installation on polyurethane foam insulation, providing a durable and protective surface. Its lightweight and flexible design ensures seamless application without compromising the foam’s insulating properties.
AMK enhances the surface’s resistance to external impacts, weather, and mechanical stress, offering long-lasting durability. The combination of polyurethane foam’s thermal insulation and AMK’s decorative finish creates an energy-efficient, aesthetically pleasing solution for both interiors and exteriors.
This pairing is perfect for projects requiring insulation with a modern, elegant cladding material.
Scheme of installation of AMK on Polyurethane Foam
- Wall
- Adhesive mortar
- Polyurethane Foam
- Basecoat and Reinforcement Mesh
- White tile glue
- AMK
5. Natural Insulation Materials
These materials are derived from renewable resources, making them ideal for sustainable building projects.
- Examples:
- Cork: Durable and lightweight, perfect for interior insulation.
- Hemp: Offers good breathability and moisture resistance.
- Sheep’s Wool: Provides excellent thermal and acoustic properties.
- Cellulose: Made from recycled paper, it is a cost-effective, eco-friendly solution.
- Applications: Internal walls, external walls, and even roofs.
- Drawbacks: Higher cost compared to synthetic options and limited availability.
5. Rigid Foam Boards (PIR and PUR)
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) and polyurethane rigid boards are highly effective insulation materials.
- Applications: Used in cavity walls, external wall insulation, and roof systems.
- Properties:
- Extremely low thermal conductivity (0.021-0.023 W/m·K).
- Thin but highly effective, saving space.
- High resistance to moisture and fire (with appropriate treatment).
- Drawbacks: Expensive and challenging to recycle.
6. Aerogel Insulation
Aerogel is an advanced material made from silica gel, known for its exceptional thermal performance.
- Applications: High-end construction projects and space-saving insulation.
- Properties:
- Thermal conductivity as low as 0.013 W/m·K.
- Ultra-thin, making it ideal for retrofits and tight spaces.
- Drawbacks: Very high cost and limited accessibility.
Key Factors for Choosing Insulation
Aerogel is an advanced material made from silica gel, known for its exceptional thermal performance.
- Thermal Resistance (R-Value): The higher the R-value, the better the insulation.
- Moisture Resistance: Vital for areas prone to dampness or high humidity.
- Fire Safety: Materials should meet fire-resistance standards for your region.
- Durability: Choose materials with long lifespans to maximize your investment.
- Sustainability: Natural materials are a better choice for eco-friendly construction.

